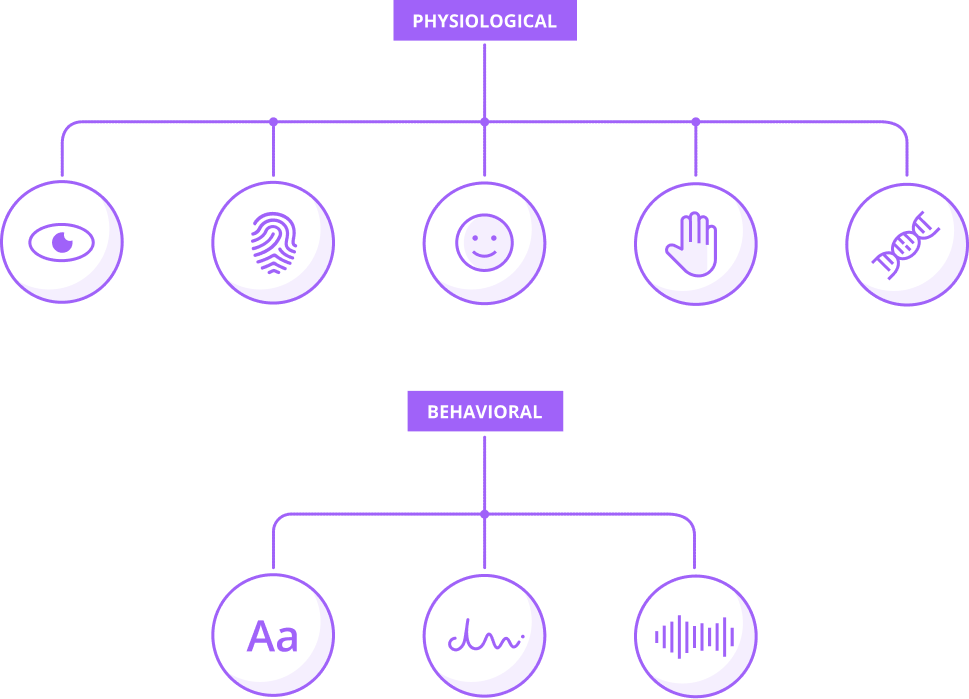
FIDO-based biometric authentication is the top choice of leading tech organizations worldwide to secure online identity. This security procedure uses unique biological characteristics. Examples of biometric authentication are retinas, irises, voices, facial features, and fingerprints to verify a person’s identity. It controls access to physical and digital resources, such as buildings and devices.
The term “biometric” combines “bio” (meaning human) and “metric” (meaning measurement). In simpler terms, biometrics are measurements related to human features that distinguish individuals from one another.
While biometric systems can handle both authentication and identification, there is a key difference between the two. Identification asks, “who are you?” while authentication asks, “Are you who you say you are?” Biometric identification confirms your identity based on your body measurements. Biometric authentication takes it a step further by comparing your information against a database to ensure you are who you claim to be.
When talking about biometric authentication we usually talk about FIDO2 authentication (an open online authentication standard built by FIDO Alliance). But is there a difference between biometric authentication and FIDO2 biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication refers to the general use of unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial features, or retinas, to verify a person’s identity.
On the other hand, FIDO2 biometric authentication is a specific implementation of biometric authentication that follows the standards and protocols set by the FIDO (Fast Identity Online) Alliance. FIDO2 incorporates strong security measures and public-key cryptography to enhance the security of biometric authentication.
FIDO2 biometric authentication offers additional benefits compared to traditional biometric authentication methods. It ensures that sensitive credentials are not exposed during the authentication process, mitigating the risk of phishing attacks or credential abuse. FIDO2 also provides a standardized approach, enabling interoperability across various devices and platforms.
In summary, while biometric authentication is a broader term encompassing various methods of using biological characteristics for identity verification, FIDO2 biometric authentication specifically refers to the implementation that adheres to FIDO Alliance standards for enhanced security and interoperability.
Companies around the world are introducing FIDO2 biometric authentication instead of other MFA methods because FIDO2 gives much better protection against phishing and credential theft comparing to all other authentication methods.
Organizations that want to introduce FIDO2 biometric authentication at scale, across the entire organization pick Secfense which makes it possible to add FIDO2 to any app within minutes and can protect entire organization with FIDO2 within days.
The word “biometrics” usually brings to mind fingerprint and eye scanners as well as face or voice recognition technology. While these are legitimate methods of biometric authentication, there is another side to biometrics called behavioral biometrics.
The difference between traditional and behavioral biometrics is that the latter authenticates continuously. It constantly monitors the users’ behavior within the application and tracks suspicious patterns. This is to make sure that the users who logged in behave like themselves. Users who act in an unusual way can be restricted from accessing further data or logged off until their identity is verified again.
Biometric authentication is often used as a major component of modern multi-factor authentication. The more security layers stand between users and applications, the more difficulty hackers face while trying to breach the organizations’ network.
While biometric multi factor authentication is much safer than passwords, relying solely on it could an enterprise in danger. For this reason, it is usually added as a second layer of security, next to passwords. Therefore, biometric authentication is a great security measure to take, as long as it is not the only one.
Biometric authentication is another approach to safeguarding data access that is a stronger alternative to passwords. Biometrics is becoming increasingly popular as the second authentication factor (in the two-factor authentication approach), with the first factor being passwords.
Why add biometric authentication to the login process? Because passwords are very unreliable in securing organization databases. Employees create weak and easy-to-guess passwords, such as “12345”, “password”, or names of their kids, spouses, or pets.
Instead of using words and numbers, biometric authentication technology uses physiological factors, such as a fingerprint, an iris, a voice, or a face, to strengthen authentication and secure access. These factors cannot be guessed. Biometric authentication solutions are often seen as the first step to passwordless authentication and are used as one of the factors in multi-factor authentication.
In the enterprise environment, biometric authentication often includes the use of some hardware authenticator. Security teams frequently incorporate hard tokens, such as FIDO2-based security keys, or local authenticators, such as smartphones and laptops that support the FIDO2 standard. With phones and laptops adapted via WebAuthn to be local authenticators, employees can use biometrics to log in. They can also use FIDO2 security keys, which are small security tokens equipped with fingerprint sensors.
Biometric authentication solutions can significantly improve remote work security. The FIDO2 standard allows organizations to take advantage of company hardware and use it as biometric authenticators. Nowadays, every smartphone and laptop has a built-in camera or fingerprint scanner so that it can be used as a biometric authentication device. Biometric authentication solutions are often integrated with privileged access management (PAM) tools and IAM platforms to ensure the most comprehensive authentication policies possible.
Biometric authentication, or any other authentication standard, can be easily deployed on any enterprise application with User Access Security Broker. The deployment is scalable, which means that this strong authentication can be activated on any application in the same way without any software development. Biometric authentication can also be used for microauthorization, adding another security layer. Enabling microauthorizations is a way to ensure that the session is continued by the user who logged in initially.
Watch how to deploy any strong authentication method using the User Access Security Broker approach: